
From left: Tang Xianrui, Guo Tonghe, Miao Xinyuan
ⅠProject Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of the new energy vehicle market, the limitations of traditional charging stations have become increasingly apparent, making it difficult to meet the environmental requirements of users for green travel. In contrast, integrated photovoltaic-storage-charging stations utilize solar power generation and energy storage technology to achieve energy self-sufficiency and renewable utilization, significantly reducing reliance on traditional power grids.
Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, with its strengths in cartographic representation, spatial analysis, and integration of spatiotemporal big data, has been widely applied across various industries. By integrating spatiotemporal big data and coupling algorithmic models, GIS technology plays a crucial role in the layout, planning, and management of integrated photovoltaic-storage-charging stations. This GIS-integrated management model not only provides strong support for the sustainable development of the photovoltaic-storage-charging industry but also promotes the adoption and application of green energy.
Futian District, located in the central part of Shenzhen, is one of the city's political, cultural, and commercial centers. In terms of new energy vehicle charging infrastructure, Futian District is a pioneer known as the "City of Supercharging," with the highest average density of charging piles in the city. It is the first district in Shenzhen to achieve more supercharging stations than gas stations, making it a new showcase for "smart photovoltaics + advanced energy storage + supercharging" in Shenzhen.
Based on this context, this study takes Futian District, Shenzhen, as a case area. Starting from the layout optimization of photovoltaic-storage-charging stations, it aims to identify the optimal site selection points through spatiotemporal data analysis, striving to fill the gap in the emerging field of "photovoltaic-storage-charging" integrated with GIS.
1. Analysis Process
1.1 Methods and Workflow
This study primarily employed GIS, Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), K-means clustering, NSGA-II algorithm, and TOPSIS algorithm to optimize the site selection of photovoltaic-storage-charging stations in Futian District, Shenzhen.
1.2 Key Results
1.2.1 Pre-Optimization Service Area Analysis
Using a topological network construction tool with road network data from the study area, existing photovoltaic-storage-charging stations were input as service points to generate and analyze service areas.
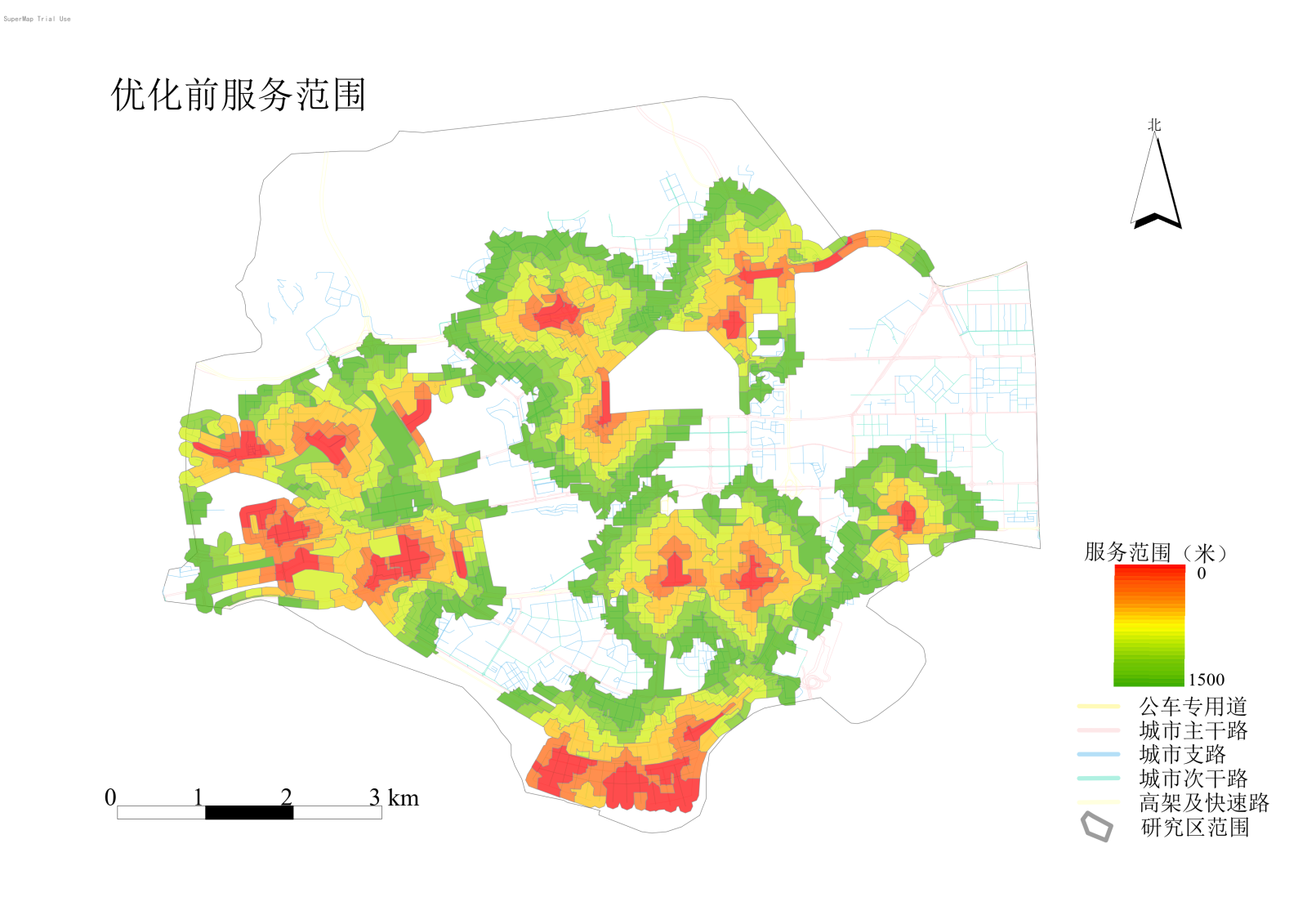
Figure 1: Pre-Optimization Service Area
1.2.2 Determining New Station Locations
A site suitability model was constructed to identify highly suitable points. These points were processed using Python code, ultimately applying K-means clustering, NSGA-II, and TOPSIS algorithms to obtain general candidate sites. A solar radiation analysis model was built to determine solar radiation conditions from 12:00 to 14:00 on the winter solstice. Existing station data was used to validate this model's accuracy.
The results of the solar radiation analysis were overlaid with the general candidate sites to derive the final dataset for new photovoltaic-storage-charging station locations.

Figure 2: Shadow Areas and Model Validation Based on Solar Radiation (12:00-14:00, Winter Solstice)
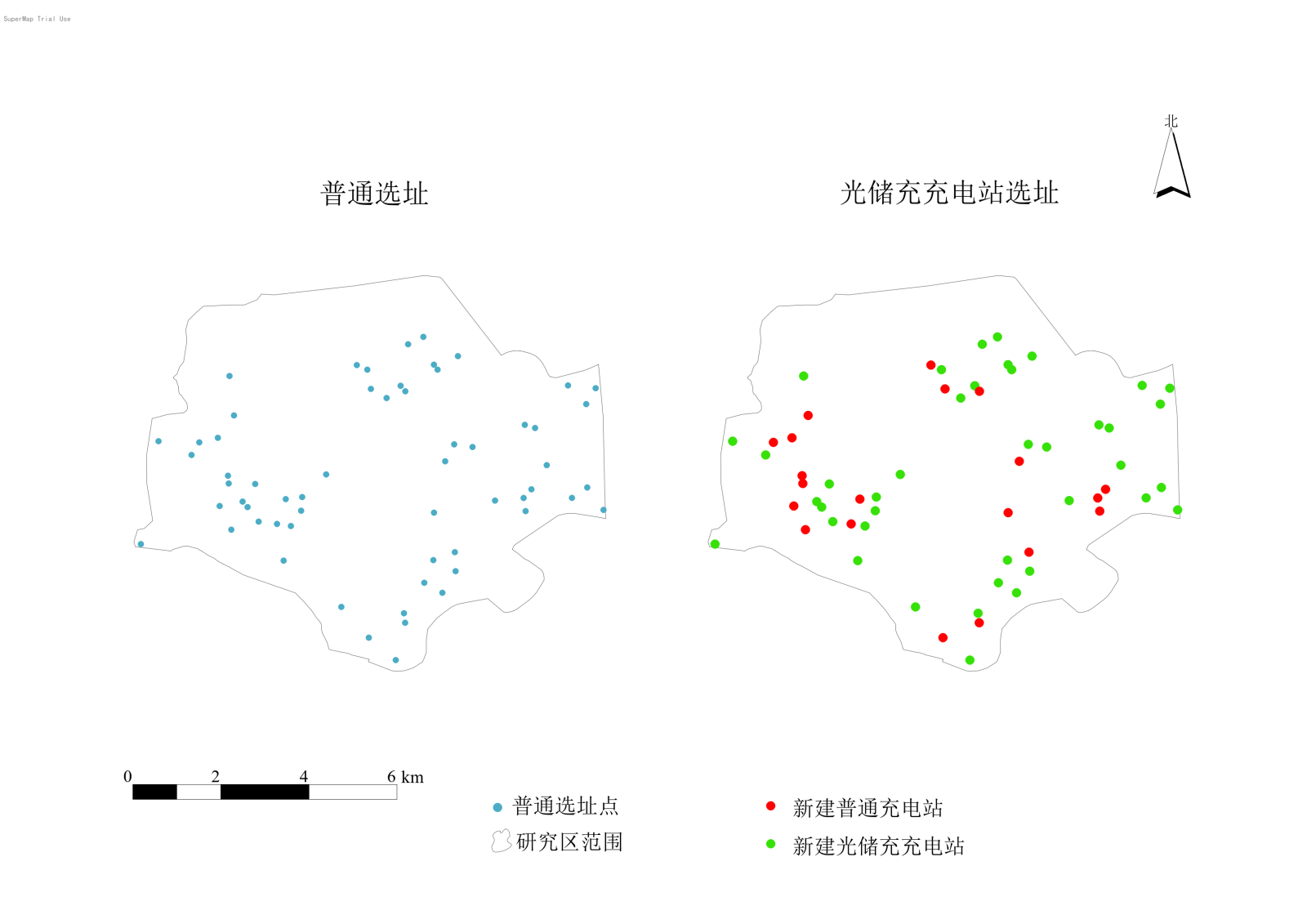
Figure 3: Site Selection Results
1.2.3 Post-Optimization Service Area Analysis
Using the topological network tool again, both existing and newly planned stations were input as service points to generate and analyze the updated service area.
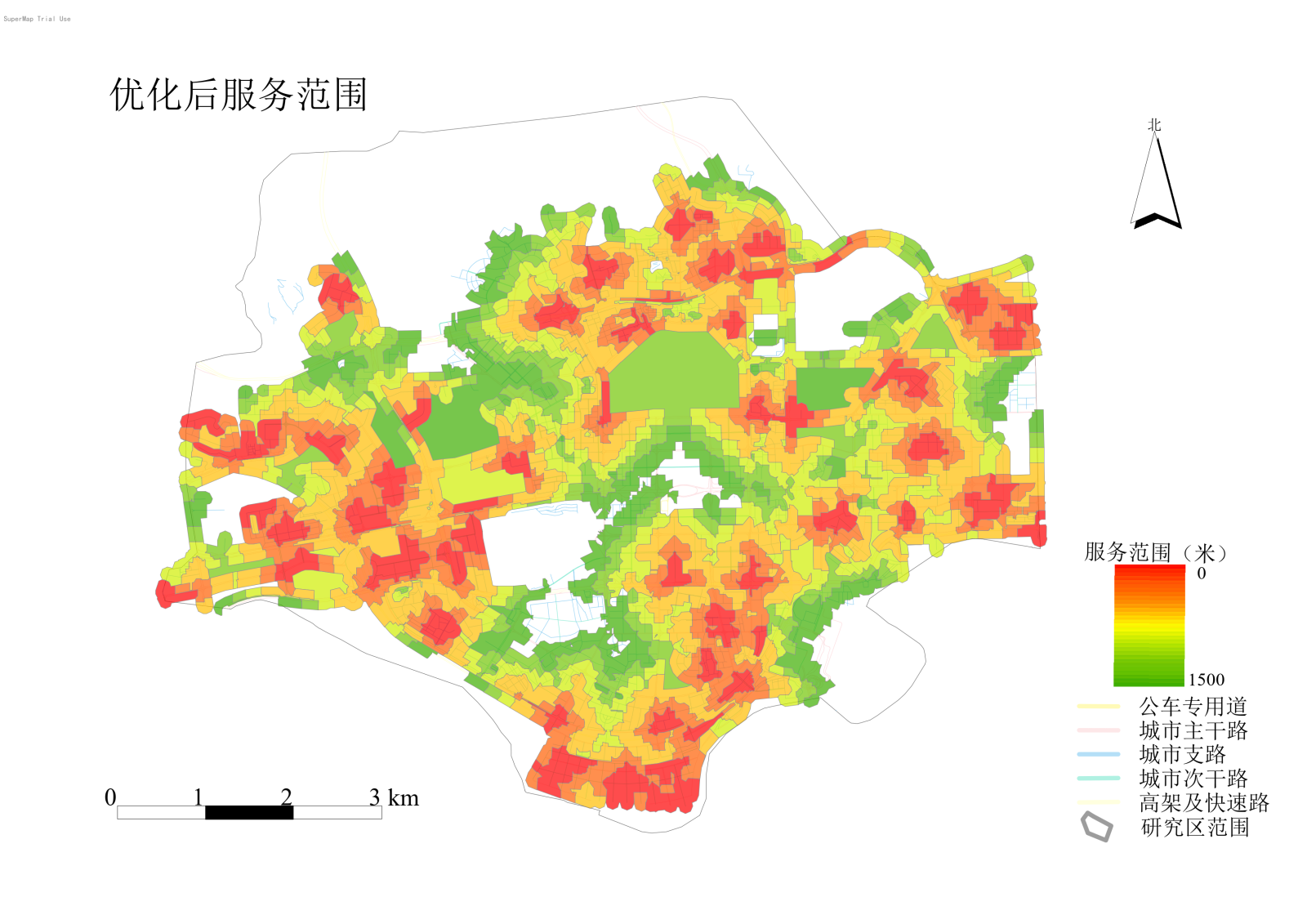
Figure 4: Post-Optimization Service Area
Ⅱ Project Highlights and Improvement Directions
1. Highlights
2. Improvement Directions
Ⅲ Advisors' Comments
This project integrates GIS technology with the layout optimization of integrated PV-storage-charging stations, providing a new research approach for planning new energy charging infrastructure. By employing various algorithms and models like NSGA-II and TOPSIS, combined with solar radiation analysis, it conducts site selection planning for PV-storage-charging stations in Futian District, Shenzhen. The research results not only offer a theoretical basis for optimizing the layout of these stations but also lay a solid foundation for promoting the adoption and application of green energy. This work holds significant scientific value and practical importance for the sustainable development of new energy infrastructure.
© 1997-2025 SuperMap Software Co., Ltd.
6/F, Building 107, No. A10, Jiuxianqiao North Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing
Links:SuperMap